WHAT IS COMPUTER NETWORK? HOW TO DIVIDE NETWORK
What is Computer Network?
Are two or more computers connected in some way so that they can exchange information with each other. The advent of computer networks stems from the need to share and share data. No network, the data on the independent computer to share with each other right through the printing or copying via floppy, CD ROM, ... this causes a lot of inconvenience to the user.
- The computer is connected to a network that allows the possibilities:
- General use utility tools
- Share shared data repository
- Improved reliability of systems
- Exchanging messages, image,
- Sharing peripherals (printer, Drawing machine, Fax, modem …)
- Reduce costs and travel time.
DISTINCTIVE KIND NETWORK
Network connection method is used mainly in networking: There are two main methods, that's the point – point and point – many points.
With methods “point – point”
The separate transmission line is set to connect the computer couples together. Each computer can transmit and receive data directly or can act as an intermediary, such as storing the data it receives and then forwards the data to go to a different machine that data reaches the destination.
With methods “point – many points”
All stations share a transmission line division physics. Data is sent from one computer can be received by all the remaining computers, so should indicate the destination address of the data to each computer based on which check data can be for yourself if true, get there otherwise ignored.
DISTRIBUTION OF COMPUTER NETWORK BY REGION
BOTH (Global Area Network):
Connected computers from different continents. Normally this connection is made via telecommunications networks and satellite.
VAN (Wide Area Network):
Wide area network, connect computers within countries or between countries in the same continent. Normally this connection is made via telecommunication networks. The WAN can be connected together into itself as GAN or GAN.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
Connect computers within a city. This connection is made through the communication medium high speed (50-100 Mbit/s). (Local Area Network) – Local area network, connected computers in an area normally narrow radius of a few meters trǎm. The connection is made through the media environment eg high-speed fiber-optic coaxial cable replacement. LANs are often used within an agency / organization…LANs can be connected together into a WAN.

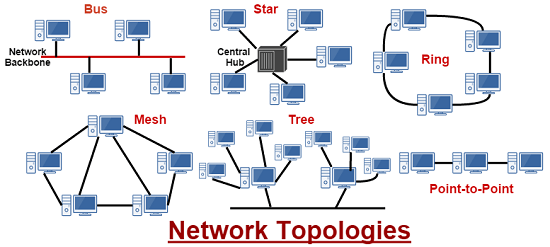
TYPES OF COMPUTER NETWORK
Star-shaped network (Star topology):
In a star formation, all stations are connected to a central device is responsible for receiving signals from the signal station and transfer to the destination station with connection method is the method “point – point”.
Network online form (Bus Topology):
In the online form, the computers will be connected to a main transmission line (bus). The main transmission line is limited both by a special connector called a terminator (used to identify the end to end transmission lines here). Each station is connected to the bus through a connector T (T_connector) or a transceiver (transceiver).
Ring network (Ring Topology):
The computers are linked together in a circular manner “point – point”, through which each station can receive and transmit data within a dimension and the data is transmitted in each packet a.
Network combinations:
In fact, depending on the requirements and specific purpose we can design a form that combines network, ring, routes to take advantage of the strengths of each.
NETWORK BY FUNCTION
Client-Server Network: one or several computers are set up to provide services such as file server, mail server, Web server, Printer server, ... The computer is set up to provide the service called Server, also computers to access and use the service, is called Client.
Peer networks (Peer-to-Peer): Computers on the network can act as both a client and a server.
Matching networks: Computers are typically set up in both Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer functions.
NETWORK DIFFERENCE – WAN NETWORK
– Local activities
+ LAN used in a small geographic area.
+ WAN for connecting computers in different geographical areas, on a wide range.
– Connection speed and bit error rate
+ LAN connection speed and reliability.
+ Speed WAN connections can not be too high to ensure the bit error rate may be acceptable.
– Communication methods:
+ LAN technology mainly uses Ethernet, Token Ring, ATM
+ WAN using multiple technologies such as switching ring (Circuit Switching Network), packet switching (Packet Switching Network), ATM (Cell relay), Switching the frame (Frame Relay), …
Maybe you are interested: Construction company office network, company, building, industrial area, factory

